在web开发中,拦截器是经常用到的功能。它可以帮我们预先设置数据以及统计方法的执行效率等等。今天就来详细的谈一下spring中的拦截器,需要的可以参考一下
1.Spring中的拦截器
在web开发中,拦截器是经常用到的功能。它可以帮我们预先设置数据以及统计方法的执行效率等等。
今天就来详细的谈一下spring中的拦截器。spring中拦截器主要分两种,一个是HandlerInterceptor,一个是MethodInterceptor。
1.1HandlerInterceptor拦截器
HandlerInterceptor是springMVC项目中的拦截器,它拦截的目标是请求的地址,比MethodInterceptor先执行。其工作原理是当请求来时先进性预处理,如下。
这里我们可以实现一个通过HandlerInterceptor实现打印请求开始和结束的日志,如下。
1.依赖引入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.实现类
拦截器类
@Component
public class EasyLogControllerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
/**
* 在controller调用之前执行
*/
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
System.out.println(request.getRequestURI()+"开始执行");
return true;
}
/**
* 在controller调用中执行
*/
public void postHandle(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView)
throws Exception {
}
/**
* 在controller调用后执行
*/
public void afterCompletion(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex)
throws Exception {
System.out.println(request.getRequestURI()+"执行结束");
}
}
controller类
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public Map<String,String> hello(){
Map<String,String> response=new HashMap<>();
response.put("msg","hello");
return response;
}
}
配置类
@Configuration
public class IntercepterConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Autowired
private EasyLogControllerInterceptor easyLogControllerInterceptor;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
//addPathPatterns用于添加拦截路径
//excludePathPatterns用于添加不拦截的路径
registry.addInterceptor(easyLogControllerInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/hello");
}
//此方法用于配置静态资源路径
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/my/");
}
}
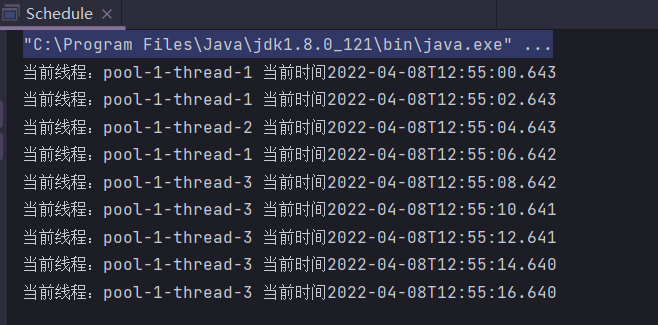
3.运行效果
1.1.1HandlerInterceptor讲解
实现一个HandlerInterceptor拦截器可以直接实现HandlerInterceptor接口,也可以继承HandlerInterceptorAdapter类。这两种方法殊途同归,其实HandlerInterceptorAdapter也就是声明了HandlerInterceptor接口中所有方法的默认实现,而我们在继承他之后只需要重写必要的方法。
下面就是HandlerInterceptorAdapter的代码,可以看到一个方法只是默认返回true,另外两个是空方法:
public abstract class HandlerInterceptorAdapter implements HandlerInterceptor {
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return true;
}
public void postHandle(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView)
throws Exception {
}
public void afterCompletion(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex)
throws Exception {
}
}
这三个方法都是干什么的,有什么作用,什么时候调用,不同的拦截器之间是怎样的调用顺序呢?
先补一张图:
这还得参考一下DispatcherServlet的doDispatch方法:
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
int interceptorIndex = -1;
try {
ModelAndView mv;
boolean errorView = false;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest, false);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String requestUri = urlPathHelper.getRequestUri(request);
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + requestUri + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// Apply preHandle methods of registered interceptors.
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = mappedHandler.getInterceptors();
if (interceptors != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
if (!interceptor.preHandle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler())) {
triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, null);
return;
}
interceptorIndex = i;
}
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Do we need view name translation?
if (mv != null && !mv.hasView()) {
mv.setViewName(getDefaultViewName(request));
}
// Apply postHandle methods of registered interceptors.
if (interceptors != null) {
for (int i = interceptors.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
interceptor.postHandle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler(), mv);
}
}
}
catch (ModelAndViewDefiningException ex) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", ex);
mv = ex.getModelAndView();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(processedRequest, response, handler, ex);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
// Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
render(mv, processedRequest, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling");
}
}
// Trigger after-completion for successful outcome.
triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, null);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// Trigger after-completion for thrown exception.
triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
ServletException ex = new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err);
// Trigger after-completion for thrown exception.
triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (processedRequest != request) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
代码有点长,但是它封装了springMVC处理请求的整个过程。首先根据请求找到对应的HandlerExecutionChain,它包含了处理请求的handler和所有的HandlerInterceptor拦截器;然后在调用hander之前分别调用每个HandlerInterceptor拦截器的preHandle方法,若有一个拦截器返回false,则会调用triggerAfterCompletion方法,并且立即返回不再往下执行;若所有的拦截器全部返回true并且没有出现异常,则调用handler返回ModelAndView对象;再然后分别调用每个拦截器的postHandle方法;最后,即使是之前的步骤抛出了异常,也会执行triggerAfterCompletion方法。
1.2 MethodInterceptor拦截器
MethodInterceptor是AOP项目中的拦截器,它拦截的目标是方法,即使不是controller中的方法。具体使用方式可以参考SpringBoot中利用AOP和拦截器实现自定义注解
2.二者的区别
上面的两种拦截器都能起到拦截的效果,但是他们拦截的目标不一样,实现的机制不同,所以有的时候适用不同的场景。
HandlerInterceptoer拦截的是请求地址,所以针对请求地址做一些验证、预处理等操作比较合适。当你需要统计请求的响应时间时MethodInterceptor将不太容易做到,因为它可能跨越很多方法或者只涉及到已经定义好的方法中一部分代码。MethodInterceptor利用的是AOP的实现机制,在本文中只说明了使用方式,关于原理和机制方面介绍的比较少,因为要说清楚这些需要讲出AOP的相当一部分内容。在对一些普通的方法上的拦截HandlerInterceptoer就无能为力了,这时候只能利用AOP的MethodInterceptor。
另外,还有一个跟拦截器类似的东西----Filter。Filter是Servlet规范规定的,不属于spring框架,也是用于请求的拦截。但是它适合更粗粒度的拦截,在请求前后做一些编解码处理、日志记录等。而拦截器则可以提供更细粒度的,更加灵活的,针对某些请求、某些方法的组合的解决方案。
另外的另外,用过人人网的ROSE框架的人都会非常喜欢它的拦截器功能。因为它实现了全注解的方式,只要在类的名字上加上拦截器的注解即表示这是一个拦截器。而使用这个拦截器的方法或者controller也只需在方法或controller的上面加上这个拦截器的注解。其实这是一个关注点的转变,spring的切面控制在配置文件中,配置文件关注哪些地方需要拦截。而在ROSE中,则是在需要拦截的地方关注我要被谁拦截。
以上就是一文了解Spring中拦截器的原理与使用的详细内容,更多关于Spring拦截器的资料请关注编程学习网其它相关文章!
本文标题为:一文了解Spring中拦截器的原理与使用


- SpringBoot使用thymeleaf实现一个前端表格方法详解 2023-06-06
- Java实现顺序表的操作详解 2023-05-19
- Springboot整合minio实现文件服务的教程详解 2022-12-03
- 基于Java Agent的premain方式实现方法耗时监控问题 2023-06-17
- 深入了解Spring的事务传播机制 2023-06-02
- JSP页面间传值问题实例简析 2023-08-03
- ExecutorService Callable Future多线程返回结果原理解析 2023-06-01
- Java中的日期时间处理及格式化处理 2023-04-18
- JSP 制作验证码的实例详解 2023-07-30
- Spring Security权限想要细化到按钮实现示例 2023-03-07